
DIFFERENCE BETWEEN TOCOTRIENOLS AND TOCOPHEROLS – TOCOTRIENOLS, THE UNAPPRECIATED VITAMIN E
Have you failed to beat the odds against deadly diseases like cardiovascular, fatty liver, and cancer? Well, worry not! You have a trustworthy but an unappreciated aid who would help you fight your battle more fiercely!
Introduction
Did you know that every day your body gets rid of at least one such cell which could have caused cancer? And, did you know what helps you in eliminating such cells out of your body? Your vitamins! Not only cancer, but other chronic ailments like cardiovascular diseases, Alzhiemer’s, Parkinson’s etc. are often prevented by certain vitamins like the Vitamin E. But did you know that Vitamin E is known to exist in 8 different forms? Four isoforms of Tocopherols and four isoforms of Tocotrienols. For several decades, researchers have studied Tocopherols for their anti-oxidative properties and other health benefits but only a few years ago they realized that Tocopherols don’t possess any of those health benefits which they were thought to possess. Dr. Barrie Tan, who has studied these Vitamins for over 35 years has described Tocopherols as a “flaw”! Anti-oxidative and anti-cancer properties of Tocotrienols have now amazed the researchers and the doctors to such an extent that Dr. Barrie Tan has quoted Tocotrienols as, “Tocotrienols, Vitamin E beyond Tocopherols” and moreover, he has also written a book on Tocotrienols with the name,” Tocotrienols, Vitamin E beyond Tocopherols”. And do you know what has made all the difference? The difference in their molecular structures!
Speaking of their structure, Tocotrienols have a smaller structure as compared to Tocopherols which increases its mobility and helps Tocotrienol target a larger area and more cells. Dr. Barrie has even designated to Tocotrienols as the “State trooper” or the protector of State due to its high mobility and large coverage area. The Tocopherols on the other hand are quite localized.
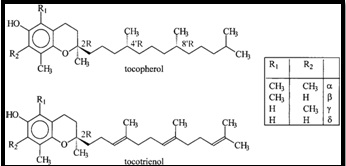
All the isoforms of both Tocopherols and Tocotrienols are made up of a chromane ring (a heterocyclic chemical compound with the formula C9H10O) with a hydroxyl group and a hydrophobic chain which allows for penetration into biological membranes like your cell membranes. Both Tocopherols and Tocotrienols exist in Alpha, Beta, Gamma and Delta forms (the four isoforms of both Tocopherols and Tocotrienols) determined by the number and position of methyl groups on the chromanol ring. Both Tocopherols and Tocotrienols exhibit Vitamin E activity and both of them are fat-soluble anti-oxidants although they have been shown to have several other functions in the body.
Edible oils are the major natural dietary sources of Tocopherols and Tocotrienols, collectively known as Tocols. Tocols have been observed to exhibit several health benefits like helping you fight certain chronic ailments, heart diseases and so on. Because of their anti-oxidant characteristics, Tocols play a major role in protecting mono- and poly-unsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) from oxidation.
Out of all the research carried out on Vitamin E, 95% of it conducted on Tocopherols while only 5% of it has been conducted on Tocotrienols. However, accumulating preclinical and clinical studies have shown that Tocotrienols display stronger anti-oxidant, anti-inflammatory, and chemopreventive activities when compared with Tocopherols!
DIFFERENCE BETWEEN TOCOPHEROLS AND TOCOTRIENOLS BASED ON OCCURRENCE
Food sources with the highest concentrations of Vitamin E include vegetable oil, nuts, and seed i.e. usually in your breakfast cereals. Speaking of Tocopherol, these are easily available at the drug stores, either alone, or in multivitamin form which you have been taking usually. Tocopherols are also known as synthetic vitamin E and you will be surprised to know that supplementation of Tocopherol is bad news! In its natural form, Tocopherol is found in palm oil, rice bran, wheat germ, soya bean oil, safflower oil, peanut oil, and cocoa butter. Tocopherol is present in your daily diet and it has been observed that consumption of too much Tocopherols is harmful for the body and moreover it hinders with the function of Tocotrienols! Only Alpha-Tocopherol has a “transport protein”, which chaperones a particular molecule to a site of action. The transport protein ensures the conservation of Alpha-Tocopherol (which is why supplementation is bad news)
On the other hand, Tocotrienols, which are also referred to as natural Vitamin E, occur naturally in very low concentrations which is quite unfortunate. They are usually found in wheat germ, saw palmetto, barley, oats, rye, rice, and bran. Although highest concentrations of Tocotrienol are found in the Annatto plant found in the Amazons. Annatto is the only plant which is 100% Tocopherol free! Jonathan Lizotte, Designs for Health Founder and Board Chairman has quoted that,
“The health benefits realized by Annatto Tocotrienol go beyond that of any other nutrient I know. It’s the one supplement I would want with me if I were stranded on a desert island! This is a change for me as after 35 years in this industry, my top desert island supplements have switched between magnesium and fish oil and now it stands firmly as Annatto Tocotrienol alone. A minimum of 150 mg per day is a must for every adult alive.”

DIFFERENCE BETWEEN TOCOPHEROLS AND TOCOTRIENOLS BASED ON STRUCTURE
Tocotrienols differ from Tocopherols in terms of their structure due to the presence of three double bonds at positions 3’, 7’, and 11’ in the side chain of the Tocotrienols. Moreover, there are 3 chiral centers in the structure of Tocopherols which is responsible for the existence of 8 stereoisomers for each Tocopherol, while each Tocotrienol has only 2 stereoisomers due to its lack of chiral centers in its side chains.

Tocopherol molecules have a long tail with no double bonds which inhibits the functional effects of the vitamin within the body thereby lowering its anti-oxidative capacity. Tocotrienols, on the other hand, have a short tail with 3 double bonds. Tocotrienols have been observed to have a smaller structure with a smaller head and smaller tail as compared to Tocopherols which has a large structure with a larger head and a larger tail. The molecular weight of Tocotrienol is also significantly much lesser that Tocopherol. These structural advantages enable Tocotrienol to cover a larger area, increase its mobility and target more cells and tissues. This unique structure of Tocotrienols enables them to perform various functions, especially anti-oxidative, with greater efficiencies.
Tocotrienols are made up of 2’d-isomers i.e. they have a stereoisomeric carbon only at the 2′ ring-tail position. The four isoforms of Tocotrienols (d-alpha, d-beta, d-gamma, and d-delta) have structures corresponding to the four Tocopherols, except with an unsaturated bond in each of the three isoprene units that form the hydrocarbon tail, whereas Tocopherols have a saturated phytyl tail.
DIFFERENCE BETWEEN TOCOPHEROLS AND TOCOTRIENOLS BASED ON ANTI-OXIDATIVE PROPERTIES
Although both Tocotrienols and Tocopherols, have been observed to exhibit anti-oxidant properties in several studies and researches it has also been observed that the naturally occurring vitamin E, Tocotrienol is a more powerful antioxidant than Tocopherol. The order of anti-oxidative properties of Tocopherols and Tocotrienols depend on several factors such as their concentration in the body, oxidation temperature, and interactions with other molecules, which may render synergistic or antagonistic effects. But, when it comes to the difference between the anti-oxidative properties of Tocotrienols and Tocopherols, it is mainly due to their structure why they have a vast difference between their anti-oxidative properties.The shorter tail of Tocotrienol enables quicker and better mobility around cells as compared to the larger tails of Tocopherols. The structure of Tocotrienols incorporates a chain of polymers that consist of unsaturated materials which gives Tocotrienols the ability to scavenge free radicals, penetrate saturated fat cells and prevent oxidative damage. Owing to these anti-oxidative properties, Tocotrienol has become a vital compound in the body’s immune system which prevents cell damage in the brain and helps prevent tumors and various types of cancers. To the contrary, Tocopherol has a much lower anti-oxidative capacity. In certain studies, it has been observed that Gamma-Tocotrienol is the most effective in preventing lipid oxidation. Several other studies have supported Gamma-Tocotrienol to be superior to others when it came to anti-oxidative properties. In a 1955 study by Dr. Lester Packer of UC Berkley, used electron-resonance spectroscopy to compare Alpha-Tocopherol and Tocotrienol and he concluded that both of them capture free radicals, to protect the lipid from oxidation. However, Tocotrienol was 50 times more effective in protecting the cell.
DIFFERENCE BETWEEN TOCOPHEROLS AND TOCOTRIENOLS BASED ON CHOLESTEROL MANAGEMENT
In several studies and research, it has been observed that Tocopherols do not have the cholesterol-lowering ability that Tocotrienols possess. Even in small doses, Tocotrienols have been observed to lower blood cholesterol levels. They have also been observed to have the ability to cleanse the arteries of accumulated cholesterol. In certain kinds of research, it has also been observed that Tocotrienols do not only prevent plaque formation in arteries but are also able to remove the plaque from arteries. To the contrary, Tocopherols have been observed to prevent plaque formation to some extent but they failed to remove the plaque accumulated in the arteries. Alpha-Tocopherol has been repeatedly observed to interfere or attenuate with the cholesterol-lowering action of Tocotrienols in several studies and research. In several studies, effective preparation for cholesterol-lowering included 15% or less Alpha-Tocopherol and 60% or more Gamma- or Delta-Tocotrienol while ineffective preparation included 20% or more Alpha-Tocopherol and 45% or less of Gamma- or Delta-Tocotrienol. Hence we can conclude that Alpha-Tocopherol even in small quantities as compared to Tocotrienols hinders the action of Tocotrienol towards lowering of cholesterol. Moreover, Tocotrienols absorb better in the body than Tocopherols and in several kinds of research, Tocopherols have been observed to prevent absorption and organ/tissue delivery of Tocotrienols. In short, we can say that Tocopherols may interfere with functions of Tocotrienols by compromising cholesterol reduction, blocking absorption and inducing Tocotrienol catabolism for the breakdown. Also, it has been observed in many cases that Alpha-Tocopherol may cause several health issues like increasing cholesterol and blood pressure, causing the premature catabolism for the breakdown of prescription drugs and many more. Moreover,
DIFFERENCE BETWEEN TOCOPHEROLS AND TOCOTRIENOLS BASED ON ANTI-CANCER ACTIVITY
It has been observed in numerous studies that Tocotrienols display stronger anti-oxidant, anti-inflammatory, and chemopreventive activities as compared to Tocopherols. It has also been observed that isoforms of Tocotrienol namely, Alpha, Beta, Gamma, and Delta-Tocotrienols are predominant for their innate anti-cancer and chemosensitizing activities and confer their anti-cancer activities independently from its antioxidant function unlike the isoforms of Tocopherols. Tocotrienol recruits to cancer cells 10 times more than Tocopherol. Tocopherol is like municipal police within a small jurisdiction while Tocotrienol is like a state trooper with far larger jurisdiction.
Studies have also suggested that Tocotrienols are more efficient than Tocopherols in abrogating various cancer-promoting pathways including 5-lipoxygenase (5 – LOX) – catalyzed eicosanoids, cyclooxygenase (COX), nuclear transcription factor – kappa B (NF – kB) and signal transducer and activator of transcription factor 3 (STAT 3), which might be due to the higher absorption of Tocotrienol by cancer cells, attributed to their unsaturated isoprenoid side chain that enhances its lipophilic property.
It several kinds of research, it has also been observed that Tocotrienols have greater potency than Tocopherols in inducing apoptosis in all kinds of cancer cells. Moreover, studies have also shown that Gamma- and Delta-Tocotrienol induce apoptosis in several tumors via distinct mechanisms that are not shared by the isoforms of Tocopherol, like induction of endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress and increased translocation of estrogen receptor beta (ER Beta) into the nucleus by serving as a ligand for ER Beta. Tocotrienols have been found to be more potent chemosensitizers as compared to Tocopherols.
Tocopherol is kind of an hindrance for Tocotrienol because it interferes with the functioning of Tocotrienol as it attenuates cancer inhibition, inhibits absorption of Tocotrienols, reduces adipose storage, and compromises cholesterol and triglyceride reduction. Tocotrienols have been observed to obstruct the proliferation of human cancer cells whereas Alpha-Tocopherol is ineffective against proliferation. Alpha-Tocopherol not only interferes with Tocotrienol functions but also antagonizes DHA’s anticancer properties and on the other hand, Gamma-Tocotrienol enhances DHA’s effect against cancer.
In a Breast Cancer clinical study, a mixture of Tocotrienol and Tocopherol was used but then Tocopherol was replaced by Gamma-Tocotrienol because it witnessed interference of Tocopherol in the functioning of Tocotrienol! Tocopherol has been observed to attenuate cancer inhibition, inhibits absorption, reduces adipose storage, and compromises cholesterol and triglyceride reduction.
In a Lung Cancer study, all isoforms of Tocotrienols have been observed to induce apoptosis in lung cancer cells through the activation of caspase-8 and mitochondrial cyt.c release. Tocotrienol was also reported to induce apoptosis in human lung adenocarcinoma that harbors Ras mutation while Tocopherol completely failed to induce apoptosis in the lung cancer study.
In Colorectal Cancer studies, it has also been demonstrated that Delta-Tocotrienol hindered hypoxia-induced VEGF and IL-8 over expression and by lowering HIF-1 alpha, thus consequently inhibiting angiogenesis in cancer cells, unlike Tocopherols.
CONCLUSION
Over the past several decades, the majority of Vitamin E research has been focused on Alpha-Tocopherol isoform whereas only 5% of the study has been carried out for Tocotrienol isoforms. But even those 5% of studies have clearly shown that Tocotrienols have higher efficacy and health benefits when compared to Tocopherols. Tocotrienols have been found to be more potent than Tocopherols against almost all kinds of diseases, cardiovascular and chronic diseases. Not only Tocotrienols have been found to be better than Tocopherols on all grounds but it has also been observed that Tocotrienols possess very effective anti-cancer properties like induction of apoptosis, suppression of cell proliferation, suppression of angiogenesis and many more. Not only anti-cancer properties but Tocotrienols have also shown quite effective functions for the suppression of cardiovascular diseases, decreasing bone density, Cataract and so on. Tocopherol is like municipal police within a small jurisdiction while Tocotrienol is like a state trooper with far larger jurisdiction.
REFERENCES
- Tocotrienols: The Promising Analogues of Vitamin E for Cancer Therapeutics
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phrs.2018.02.017
- Annato: Delivering Tocotrienols from Amazonia, by Barrie Tan, Founder, &Anne Trias, Product Director
- Tocotrienols: Vitamin E for Cardiovascular benefits after all by Barrie Tan, Ph.D., and Anne M. Trias, MS.
- Delta-tocotrienol inhibits non-small-cell lung cancer cell invasion via the inhibition of NF-κB, uPA activator, and MMP-9.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30100736
© Copyright Fight Cancer with Vitamin E